01964 544480 / info@samuelkendall.co.uk
Scarborough Hill House
Scarborough, North Yorkshire
2019-Present
Under Construction
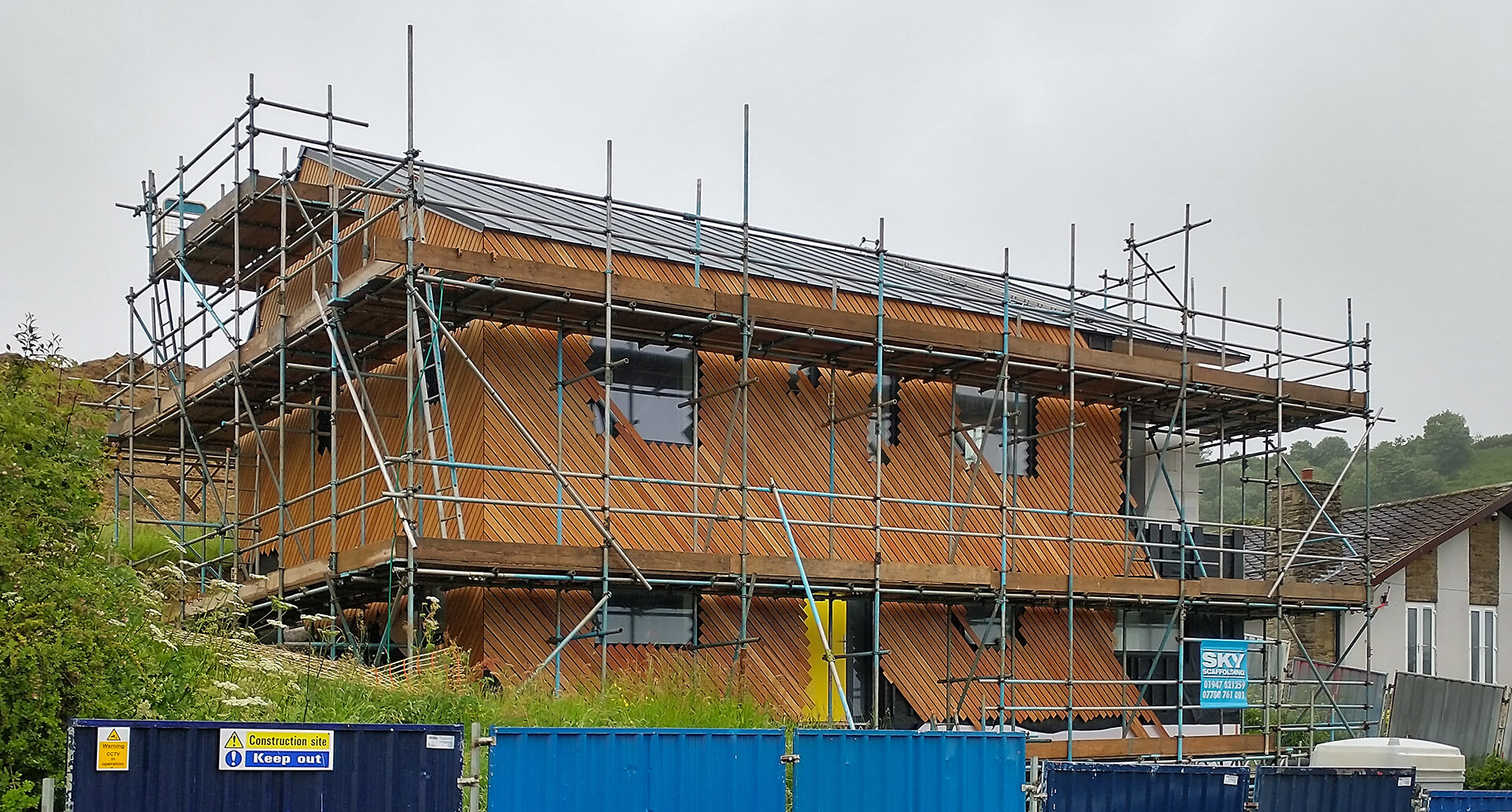
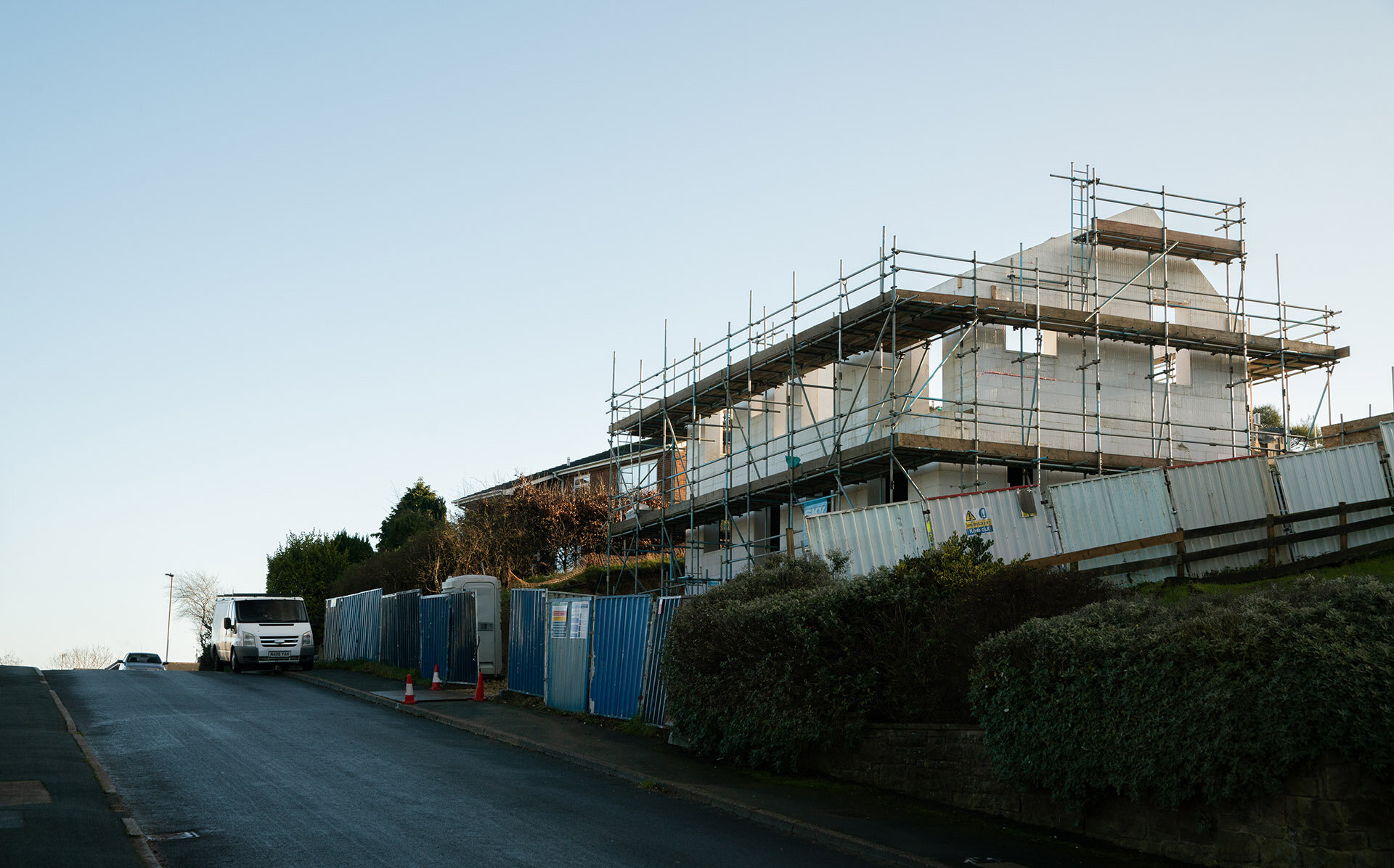
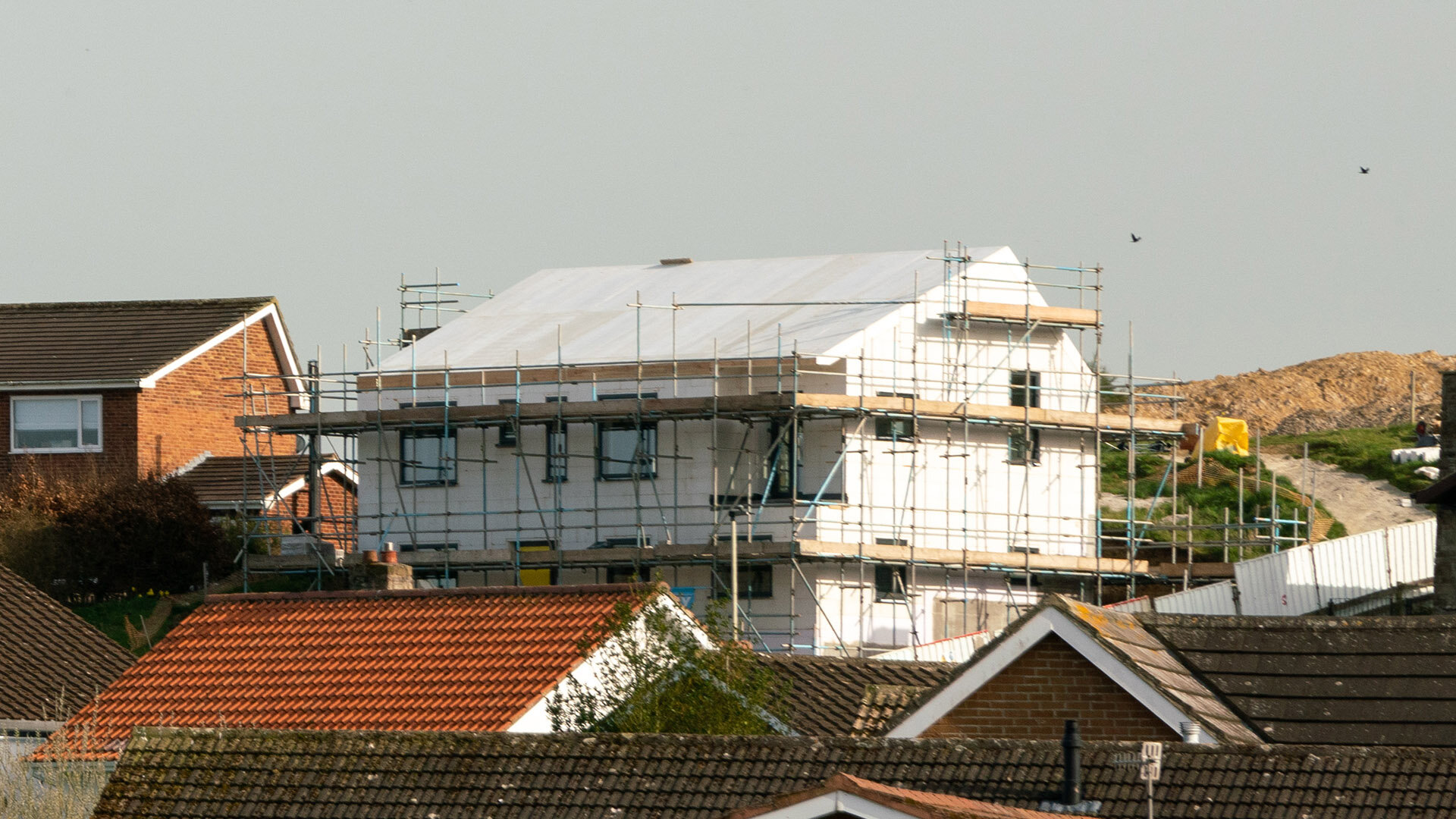
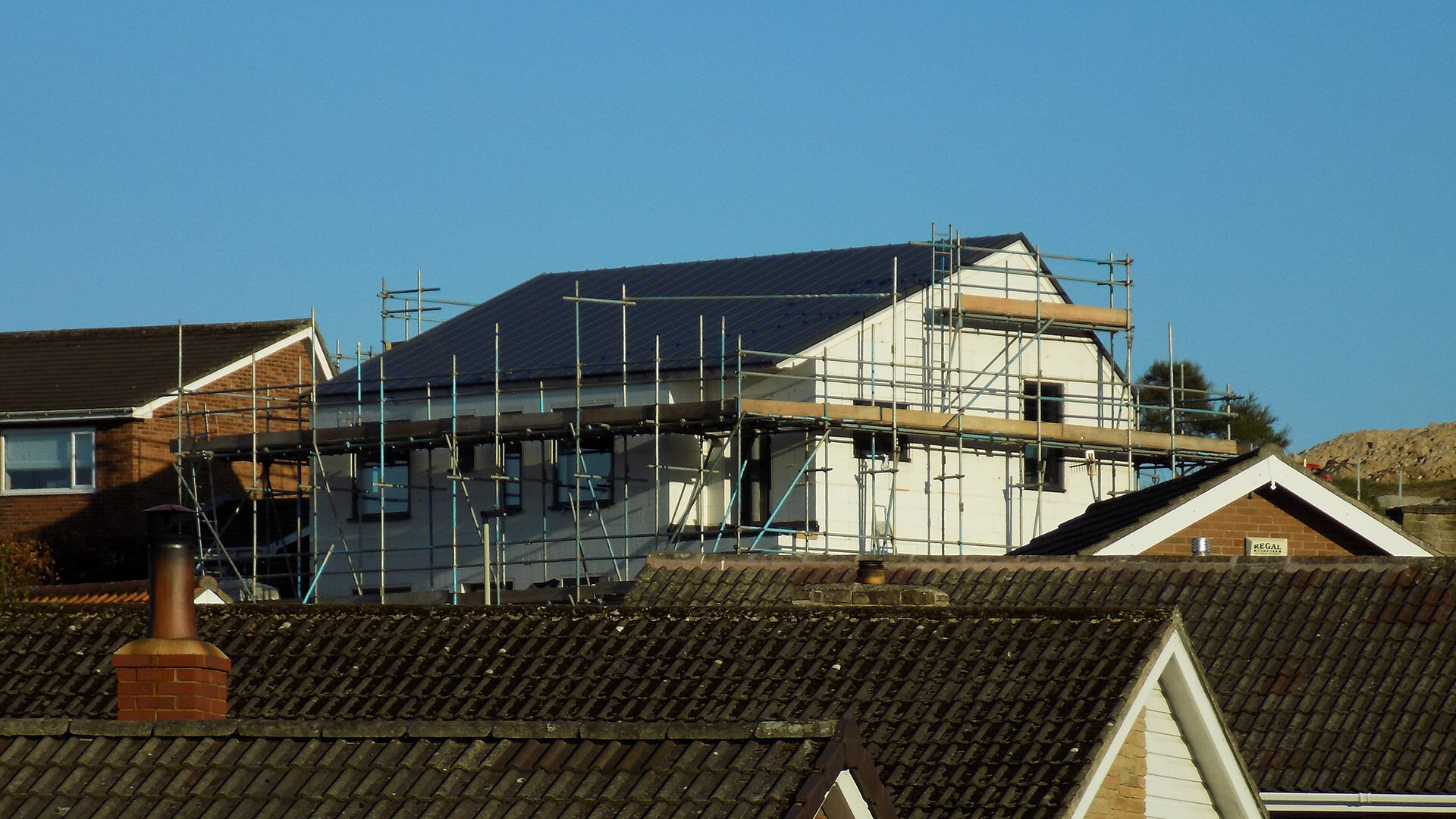
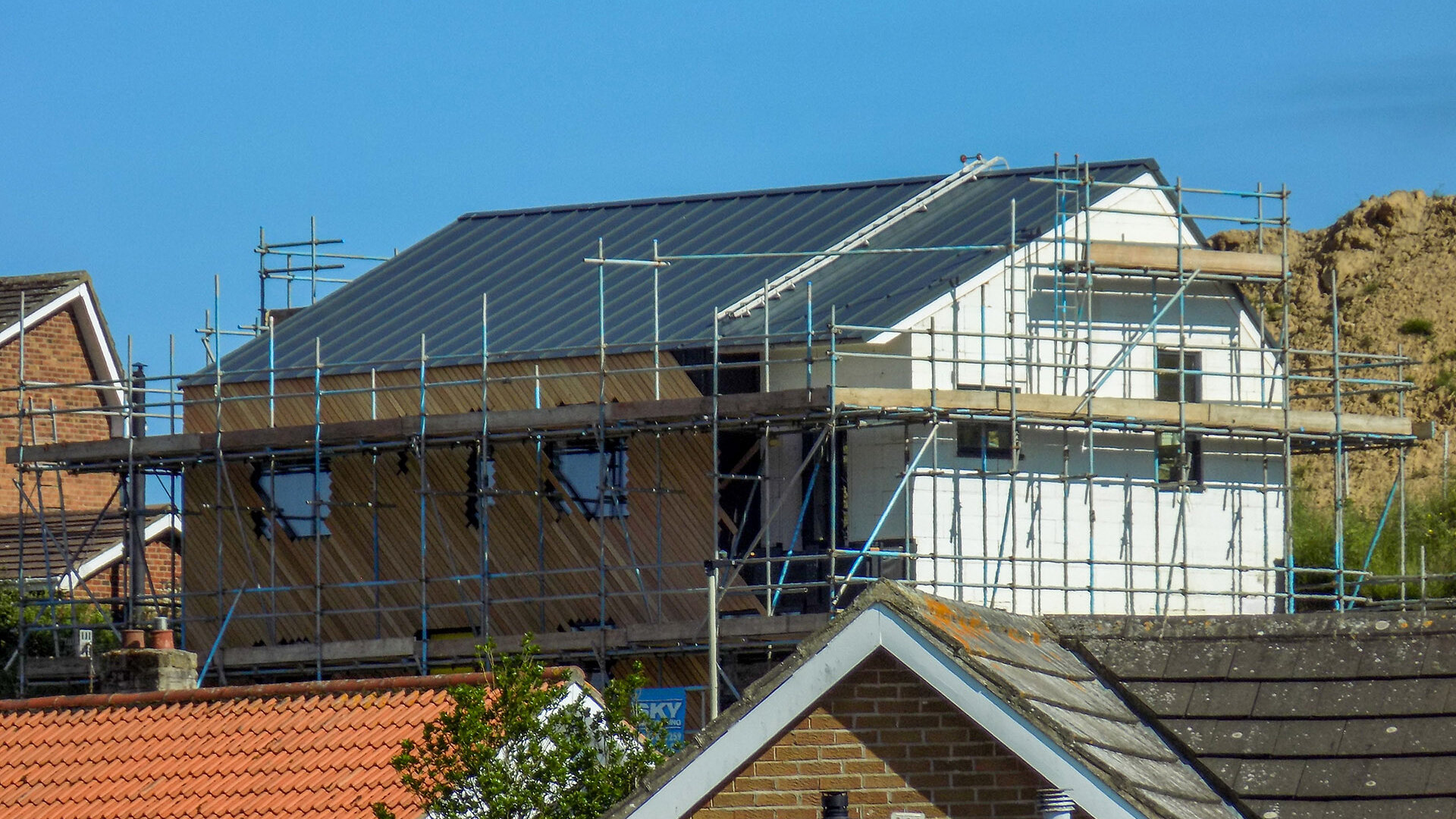
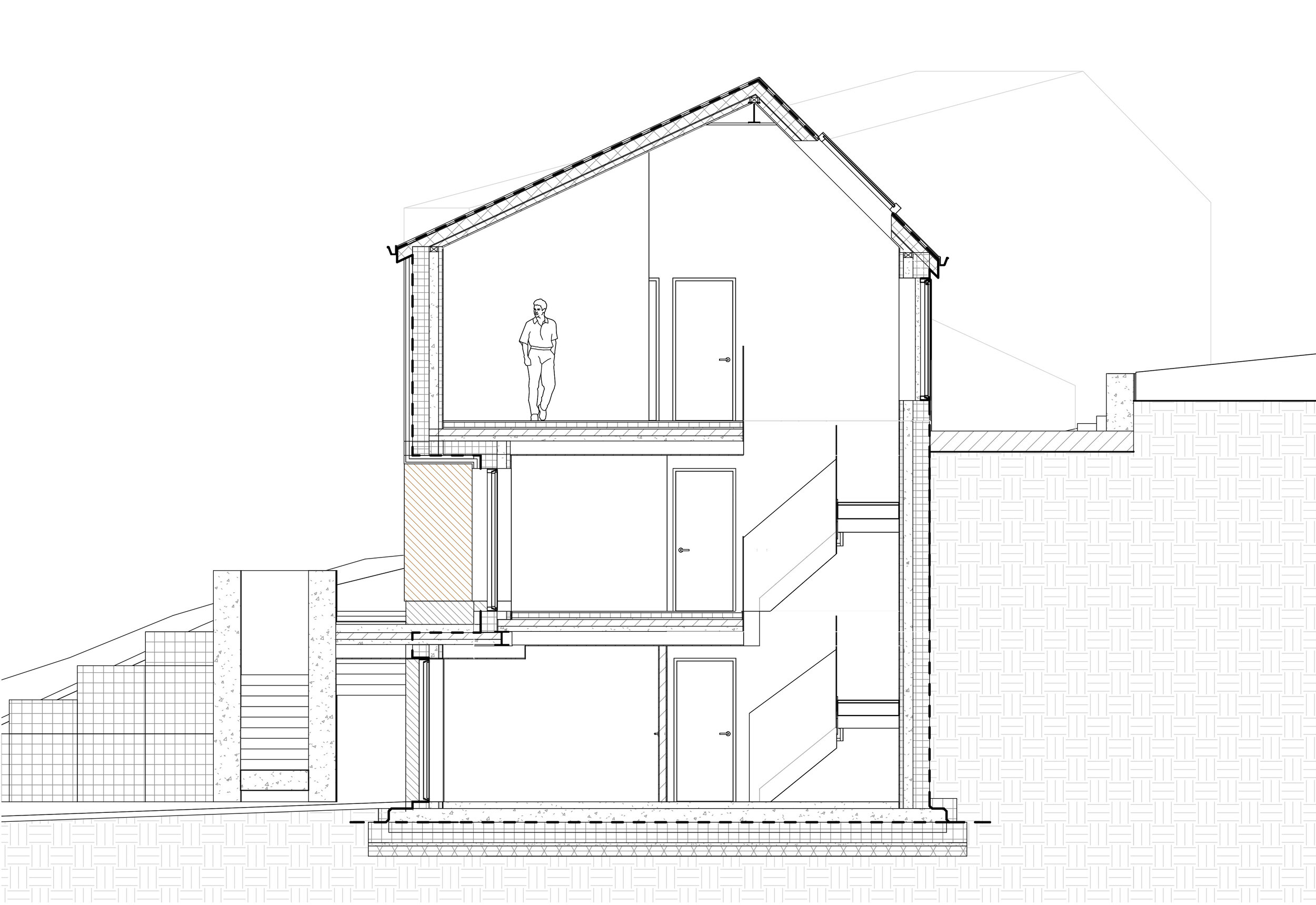
Embedded into the steep topography of Box Hill, this home enjoys panoramic views across Scarborough town centre. The setting is characterised by a line of distinct homes each defined by their era. The house is defined by its steep slope appearing from the street as a 3 storey townhouse, but only as a bungalow from the rear garden.
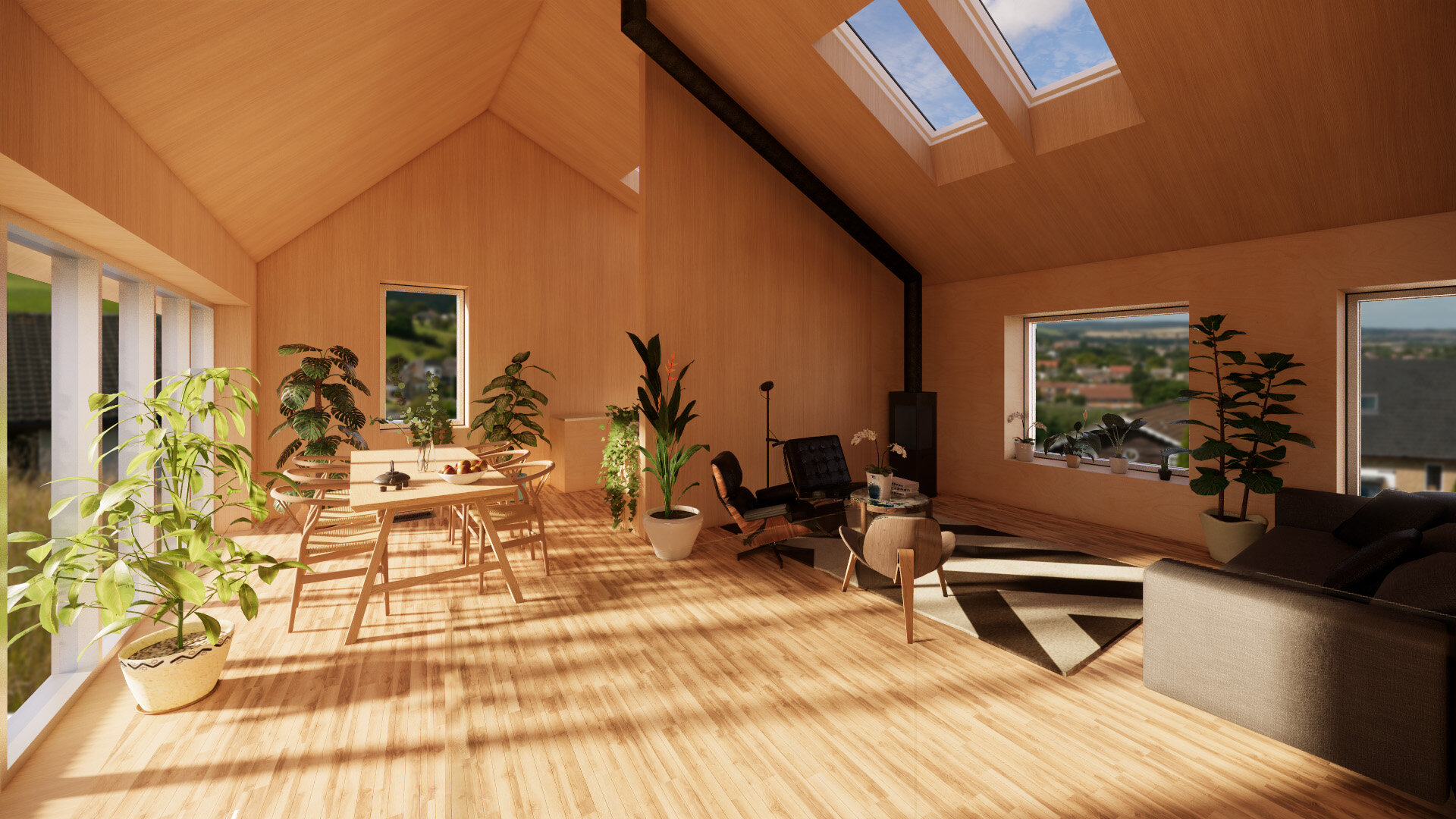
This innovative eco-home showcases the process of self-building a contemporary family home that achieves the Passivhaus standard. The home will have minimal heating & electricity costs, harvest solar energy to photovoltaic panels and bring sunlight deep into the home through a central atrium which allows the building to breathe through natural stack ventilation.
“At Samuel Kendall Associates we passionately specialise in highly sustainable homes which use the elements around them to provide a highly sustainable quality of life.”
Planning Approach.
The National Planning Policy Framework (NPPF, revised in July 2018) sets out a clear series of points in favour of sustainable development.
Paragraphs 11-15, 49 as well as many others directly address the presumption for the sustainable development of our homes and communities.
Paragraph 14 of the NPPF states:-
“At the heart of the National Planning Policy Framework is the presumption in favour of sustainable development which should be seen as the Golden Thread running through both plan-making and decision-taking”.
Paragraph 49 of the NPPF states:
“Housing applications should be considered in the context of the presumption in favour of sustainable development...”
Paragraphs 186 + 187 go further, stating:
“planning should approach decision-taking in a positive way to foster the delivery of sustainable development ... look for solutions rather than problems and ...seek to approve applications for sustainable development where possible”.
Sustainability Strategy.
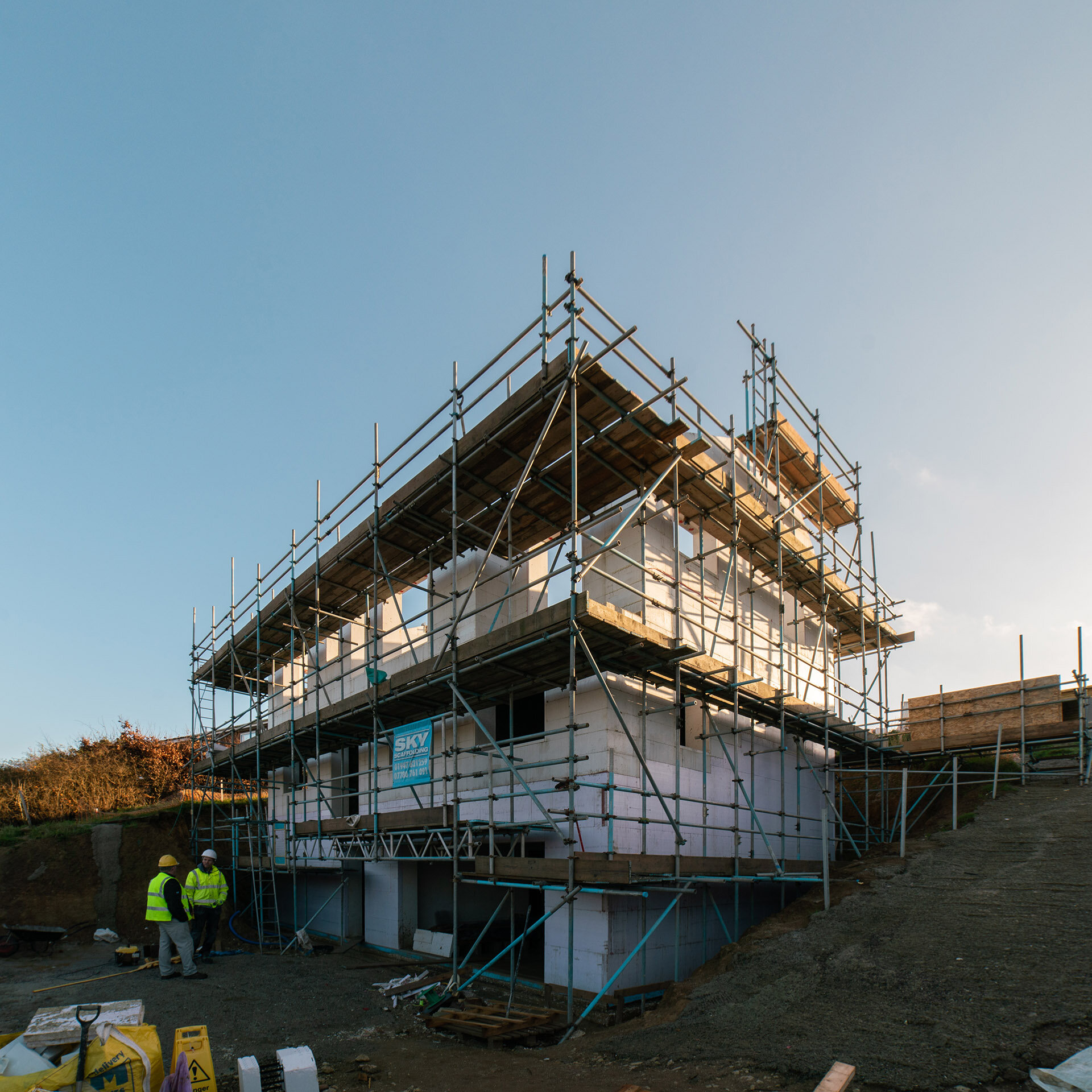
This net-zero house engages the site’s earth-sheltering hillside to minimise heat loss, optimises the home’s solar orientation and engages a host of passive solar design techniques including thermal mass heat retention, natural stack and cross ventilation and optimal levels of solar gain. The home is also built with an extremely high-performance construction method of insulated concrete formwork, surpassing thermal efficiency levels of current building regulations (0.18 W/m²K) and the Passivhaus standard (0.15 W/m²K) achieving a U value of 0.11 W/m²K.
The ICF system also enables high levels of airtightness, reaching less than 1m³/hr/m², well below the building regs requirement of 4m³/hr/m², as well as providing a thermal bridge-free form of construction, a critical factor in achieving a Passivhaus standard home.
This new family home increases the density of Scarborough’s built fabric, supporting sustainable modes of travel with ample connection to pedestrian paths and local bus routes and will also include charging infrastructure for electric vehicles as well as providing energy storage for the house.
Passive + Active Energy Systems.
The roof of this hillside home is optimally angled for solar energy absorbed by a 6kW solar PV array, which supplies a portion of the home’s electricity demand whilst also running a sophisticated MVHR (mechanical ventilation heat recovery) system. The MVHR provides a constant supply of pre-heated fresh air that retains 93% of the heat of exhausted air, drastically lowering the building’s heating demand.
The warmth of the sun is also absorbed by the dwelling’s thermally massive concrete structure, storing free heat during the day to release during the cooler evening hours, mediating any sudden changes in temperature. The highly efficient thermal wrap of the house, achieved with an insulated Atlas ground floor slab, ICF walls, triple-glazed thermal break windows and a 0.09 W/m²K SIPS panel roof negates the need for any central heating in this passive solar house.